As a medical practice owner, you’re facing an unprecedented challenge: protecting your patients’ sensitive health information while maintaining efficient operations in an increasingly digital healthcare environment. With healthcare data breaches costing an average of $4.88 million per incident and cyberattacks against healthcare organizations increasing by 32% in recent years, understanding healthcare cybersecurity compliance isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about protecting your practice’s reputation, financial stability, and your patients’ trust.
Whether you’re considering implementing your first formal cybersecurity program or evaluating your current security measures ahead of a potential practice sale, choosing the right cybersecurity framework can feel overwhelming. The good news is that you don’t need to become a cybersecurity expert to make informed decisions about protecting your practice. This guide will walk you through the most important healthcare cybersecurity frameworks and provide clear comparisons to help you understand which approach best fits your practice’s size, resources, and compliance requirements.
Key Insight: Medical records sell for $250+ on the black market compared to just $5 for credit card numbers, making your practice a high-value target regardless of size.
What Is Healthcare Cybersecurity and Why Should You Care?
Healthcare cybersecurity encompasses all the strategies, practices, and technologies you need to protect your practice’s systems, patient data, and medical devices from cyberattacks while ensuring you can continue delivering quality patient care. Think of it as a comprehensive security system for your digital practice—just as you wouldn’t leave your physical office unlocked overnight, you can’t leave your electronic systems unprotected.
For your practice, healthcare data security means protecting three critical areas:
| Security Area | What It Includes | Why It Matters |
| Electronic Health Records (EHRs) | Medical histories, diagnoses, medications, personal identifiers | Breach violates HIPAA and destroys patient trust |
| Medical Devices and Equipment | Digital X-ray machines, patient monitors, connected equipment | Entry points for cybercriminals that can impact patient safety |
| Network Infrastructure | Clinical workstations, administrative systems, Wi-Fi networks | Ensures only authorized access while maintaining connectivity |
Each connected medical device in your practice represents a potential entry point for cybercriminals. Modern healthcare IT security must protect both data and patient safety.
The reality is that cybercriminals specifically target healthcare practices because medical records are worth significantly more on the black market than other types of personal information. A single medical record can sell for $250 or more, compared to just $5 for a credit card number. This makes your practice an attractive target, regardless of its size.
Understanding Healthcare Cybersecurity Compliance Requirements
Healthcare cybersecurity compliance primarily revolves around HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) requirements, but the landscape is more complex than many practice owners realize. While HIPAA provides the foundational privacy and security standards, it was written before today’s sophisticated cyber threats emerged, creating gaps that modern cybersecurity frameworks help address.
Under HIPAA’s Security Rule, you’re required to implement “reasonable and appropriate” safeguards to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). However, HIPAA doesn’t specify exactly what technologies or procedures you must use—it’s a risk-based approach that depends on your practice’s specific circumstances, including its size, complexity, and available resources. A strong compliance posture is a key factor during the due diligence process.
Key HIPAA Compliance Facts You Need to Know:
- Penalty Range: HIPAA violations range from $100 to $50,000 per incident
- Risk-Based Approach: No one-size-fits-all requirements
- Documentation Required: You must be able to demonstrate your security efforts
- Regular Updates Needed: Security measures must evolve with new threats
- Staff Training Mandatory: All employees must understand their security responsibilities
Compliance Reality Check:
HIPAA compliance means what’s required for a 5-doctor practice differs significantly from a 50-doctor practice. The key is documenting your risk-based decisions.
The key point is that compliance isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about building a comprehensive security posture that protects your practice’s operations, reputation, and financial stability while ensuring you can continue providing quality patient care.
The Most Essential Function of Healthcare Cybersecurity
If you’re wondering where to focus your cybersecurity efforts first, the answer is clear: access control and user authentication represent the most essential function of healthcare cybersecurity for medical practices. This foundation determines who can access your systems and patient data, making it your first and most critical line of defense.
Priority Focus: Access control is your #1 cybersecurity priority because most healthcare data breaches involve unauthorized access—either from external attackers stealing credentials or internal users exceeding their authorized scope.
Access control in healthcare means ensuring that each person in your practice can only access the minimum necessary information they need to do their job—no more, no less. For example, your front desk staff needs access to scheduling and basic patient demographics, but they don’t need access to detailed clinical notes or lab results.
Essential Access Control Components:
- User Authentication: Multi-factor authentication requiring two or more verification forms
- Role-Based Access: Permissions based on specific job responsibilities
- Regular Access Reviews: Periodic audits of who has access to what information
- Audit Logging: Tracking who accesses information and when
- Immediate Access Revocation: Removing permissions when roles change or staff leave
The reason access control is so fundamental is that most healthcare data breaches involve some form of unauthorized access—whether from external attackers who steal credentials or internal users who access information beyond their authorized scope.
Understanding the Major Healthcare Cybersecurity Frameworks
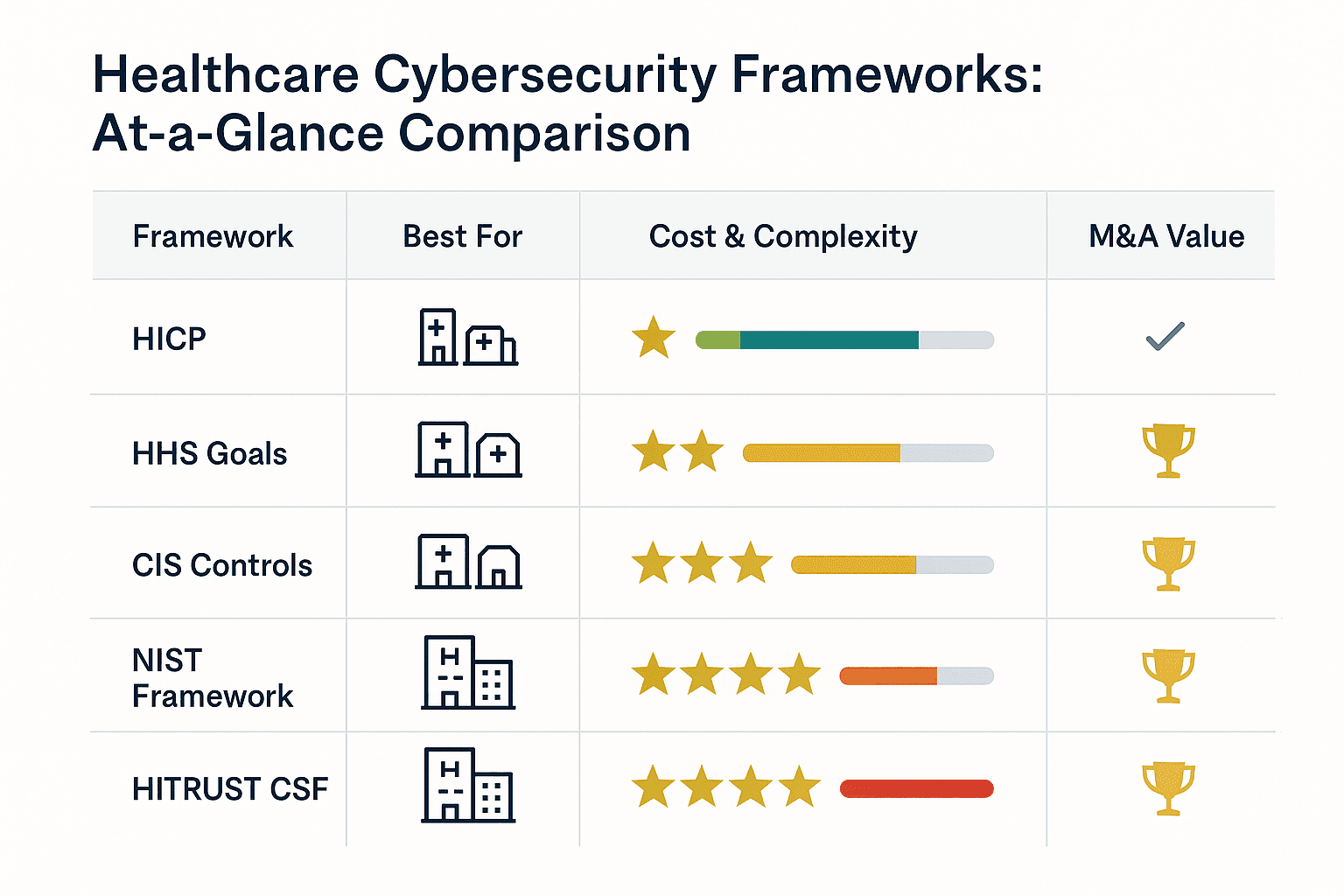
Before you can choose the right approach for your practice, you need to understand the key cybersecurity frameworks available to healthcare organizations. Each framework takes a different approach to protecting healthcare data and systems, with varying levels of complexity, cost, and regulatory focus.
Framework Selection Tip: Start with your practice size and resources, then consider your business relationships. Working with health systems? You may need HITRUST certification regardless of your practice size.
Let’s examine the five most important frameworks you should consider in detail.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The Foundation for Healthcare Practices
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework has become the gold standard for healthcare cybersecurity compliance, and for good reason. Originally developed for critical infrastructure protection, this framework provides a comprehensive yet flexible approach that works particularly well for medical practices of all sizes.
What makes the NIST framework so appealing for healthcare practices is its risk-based approach. Rather than prescribing specific technologies or procedures, it helps you organize your cybersecurity activities around six core functions:
The Six NIST Framework Functions
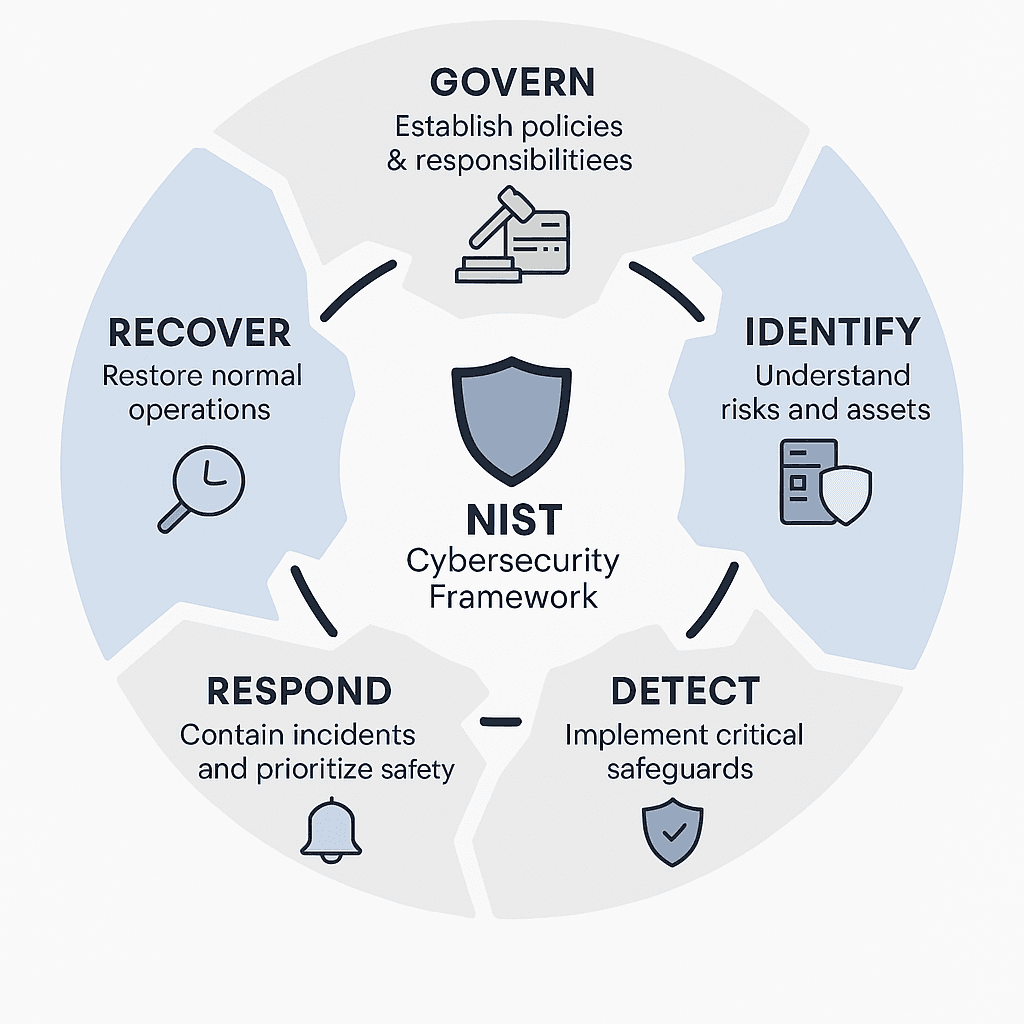
Function | What It Means for Your Practice | Example Activities |
| Govern | Establish cybersecurity policies and assign responsibilities | Designate security officer, create password policies |
| Identify | Understand your cybersecurity risks and assets | Catalog devices, identify where patient data is stored |
| Protect | Implement safeguards for critical services | Access controls, staff training, data encryption |
| Detect | Establish systems to identify cybersecurity events | Antivirus software, staff reporting procedures |
| Respond | Create procedures for containing incidents | Incident response plans prioritizing patient safety |
| Recover | Develop capabilities to restore normal operations | Data recovery procedures, lessons learned processes |
Insurance Benefit: Healthcare organizations using the NIST framework report lower cybersecurity insurance premium increases year over year compared to those using other frameworks.
Recent research shows that healthcare organizations using the NIST framework as their primary cybersecurity approach report lower cybersecurity insurance premium increases year over year compared to those using other frameworks. The framework also aligns well with HIPAA requirements, making it an attractive choice for practices seeking to address both cybersecurity best practices and regulatory compliance through a single approach.
HITRUST Common Security Framework: Comprehensive Healthcare-Specific Protection
The Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST) Common Security Framework stands out as the most comprehensive healthcare-specific cybersecurity framework available. HITRUST was specifically designed for healthcare organizations, integrating requirements from HIPAA, HITECH, NIST, ISO 27001, and other relevant standards into a single, unified framework.
The framework encompasses 19 distinct domains covering all aspects of healthcare information security, from technical controls like endpoint protection and network security to administrative measures covering risk management and incident response.
HITRUST Certification Levels:
| Certification Type | Best For | Validation Level | Typical Cost | Time Required |
| Self-Assessment | Small practices | Internal validation | $5,000-$15,000 | 3-6 months |
| Risk-Based Assessment | Medium practices | Streamlined external review | $15,000-$50,000 | 6-9 months |
| Validated Assessment | Large practices/Health systems | Full third-party validation | $50,000-$200,000+ | 12-18 months |
Many healthcare organizations now require their business associates to maintain HITRUST certification, making it increasingly important for practices that work with hospitals, health systems, or large medical groups.
HITRUST certification can significantly increase your practice’s value during a sale, demonstrating sophisticated cybersecurity management to potential buyers.
Health Industry Cybersecurity Practices (HICP): Practical Guidance for Small Practices
The Health Industry Cybersecurity Practices (HICP) guide represents perhaps the most practical and accessible cybersecurity framework specifically designed for smaller healthcare practices. What makes HICP particularly valuable for practice owners is its threat-focused approach.
The Five Primary Threats HICP Addresses:
- Email Phishing Attacks: The most common entry point for cybercriminals
- Ransomware: Attacks that can completely shut down practice operations
- Loss or Theft of Equipment or Data: Physical security concerns including stolen devices
- Accidental or Intentional Data Loss: Both honest mistakes and intentional data theft
- Attacks Against Connected Medical Devices: Vulnerabilities in networked medical equipment
Small Practice Focus: HICP is specifically designed for practices with limited cybersecurity expertise, providing maximum protection for minimal investment.
For each threat category, HICP provides implementation guidance scaled for small, medium, and large organizations. The small practice recommendations focus on fundamental security measures that provide maximum protection for minimal investment.
HHS Healthcare and Public Health Cybersecurity Performance Goals
The Department of Health and Human Services’ Healthcare and Public Health (HPH) Cybersecurity Performance Goals represent the federal government’s latest guidance specifically tailored for healthcare organizations. These voluntary goals provide a clear roadmap for healthcare practices to improve their cybersecurity resilience.
The Two-Tier Structure:
| Goal Tier | Purpose | Focus Areas | Implementation Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Essential Goals | Minimum foundational practices | Email security, endpoint protection, access control, basic incident response | Immediate (0-6 months) |
| Enhanced Goals | Advanced cybersecurity measures | Threat intelligence, advanced monitoring, supply chain risk management | Long-term (6-24 months) |
Federal Alignment: Following HHS goals demonstrates alignment with federal healthcare cybersecurity expectations, which can be valuable for practices working with government programs like Medicare Advantage
The goals have been mapped to other cybersecurity frameworks, including the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and CIS Controls, allowing you to leverage existing cybersecurity investments while addressing healthcare-specific requirements.
CIS Controls: Prioritized Security Actions
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls provide a prioritized set of actions that collectively form a defense-in-depth set of best practices. The framework consists of 18 controls organized into three implementation groups.
CIS Implementation Groups:
- Implementation Group 1 (IG1): Essential cyber hygiene practices for small practices with limited cybersecurity expertise
- Implementation Group 2 (IG2): Practices for medium-sized practices with moderate cybersecurity programs
- Implementation Group 3 (IG3): Advanced practices for large practices with mature cybersecurity programs
Data-Driven Approach: CIS Controls are prioritized based on real-world attack data, ensuring you implement the most effective security measures first.
The CIS Controls are particularly valuable because they’re prioritized based on real-world attack data, ensuring that you implement the most effective security measures first.
Framework Comparison: Which Is Right for Your Practice?
Now that you understand the major frameworks available, let’s compare them across the factors that matter most to medical practice owners. This detailed comparison will help you make an informed decision based on your specific circumstances and objectives.
Regulatory Alignment and Business Value
HIPAA Compliance Strength:
- HITRUST CSF: Specifically designed to integrate HIPAA with other standards
- NIST Framework: Strong alignment with published HIPAA crosswalk
- HICP: Healthcare-focused with HIPAA considerations
- HHS Goals: Federal healthcare guidance addressing HIPAA
- CIS Controls: General security framework requiring HIPAA overlay
Market Recognition and Business Benefits:
| Framework | Industry Recognition | Insurance Benefits | Competitive Advantage | M&A Value |
| HITRUST CSF | Highest in healthcare | Significant premium reductions | Strong differentiator | High value add |
| NIST Framework | Broad across industries | Moderate premium benefits | Good positioning | Moderate value |
| HICP | Limited external recognition | Minimal direct benefits | Shows due diligence | Basic protection |
| HHS Goals | Growing government recognition | Emerging benefits | Federal alignment | Compliance demonstration |
| CIS Controls | Technical community respect | Some premium benefits | Technical credibility | Operational strength |
Choosing the Right Framework for Your Practice
Based on our comprehensive analysis, here are our specific recommendations for different practice situations:
Recommendations by Practice Profile:
Healthcare practices should choose cybersecurity frameworks based on their size and needs. Small practices should start with HICP and HHS Essential Goals, while medium practices should use the NIST Framework with HICP details. Large practices and those preparing for sale should focus on HITRUST CSF, building on NIST. Practices with urgent compliance needs should prioritize HHS Essential Goals before moving toward NIST or HICP. Implementation timelines and costs vary, ranging from 1–18 months and $5,000 to over $200,000, depending on practice size and requirements.
Quick Start Recommendation: If you’re unsure where to begin, start with HHS Essential Goals for immediate risk reduction, then build toward your chosen long-term framework to prepare your medical practice for sale.
Implementation Priority
Regardless of which cybersecurity framework is chosen, it is essential to begin by focusing on high-impact security measures.
In the first three months, healthcare practices should establish a strong foundation by implementing multi-factor authentication for all user accounts, setting up basic email security filtering, creating and testing reliable data backup procedures, providing staff with basic security awareness training, and documenting current systems and data flows.
Quick Win: Completing these essential steps within 90 days delivers immediate risk reduction and sets the stage for long-term cybersecurity success.
From months four to six, organizations should enhance their protection by deploying endpoint protection on all devices, segmenting networks for medical devices, developing incident response procedures, conducting vulnerability assessments, and establishing regular access control reviews.
As your security posture matures—typically between months seven and twelve—more advanced capabilities can be introduced. This includes implementing continuous monitoring tools, developing comprehensive security policies, conducting penetration testing, establishing a vendor risk management program, and, if appropriate, pursuing formal certification under the chosen framework.
By following this structured, phased approach, healthcare practices can achieve effective risk reduction and build a robust cybersecurity foundation.
Success Metric: Focus on implementing the first 5 essential foundation items within 90 days—these provide the highest risk reduction for your investment and are critical for a clean Quality of Earnings (QoE) analysis.
Getting Help When You Need It
Remember that you don’t need to become a cybersecurity expert to protect your practice effectively. Many specialized healthcare consultants can help you implement appropriate security measures while you focus on providing excellent patient care. The key is taking the first steps and building from there.
When to Consider External Help:
- Implementing complex frameworks like HITRUST or comprehensive NIST
- Conducting security assessments or penetration testing
- Developing incident response capabilities
- Preparing for formal certifications
- Managing compliance documentation with help from
- IT/EHR specialists
Your patients trust you with their most sensitive health information, and implementing appropriate cybersecurity measures helps ensure that trust is well-placed. Whether you start with basic security improvements or pursue comprehensive framework implementation, taking action to protect your practice and patients is both a professional responsibility and a sound business decision.
We’re always happy to help practice owners navigate these important decisions. If you’d like to discuss how cybersecurity considerations might impact your practice’s value or preparation for a potential sale, let us know—we understand both the healthcare and cybersecurity landscapes and can help you make informed decisions about protecting your practice’s future.
Next Steps: Ready to enhance your practice’s cybersecurity posture? Schedule a consultation with our healthcare M&A advisory team to discuss your specific needs and timeline.



